Intradermale Akupunktur bei mittelschwerer bis schwerer Trockenheit der Augen: eine randomisierte kontrollierte Pilotstudie
Abstract
Objectives
The aim of this study was to evaluate the efficacy of intradermal acupuncture for the treatment of moderate to severe dry eye disease (DED).
Methods
Thirty patients with moderate to severe DED were randomly assigned (11) to either the Intradermal Acupuncture Group (IAG) or the Body Acupuncture Group (BAG). Both groups received 12 treatment sessions over four weeks (three times per week). The primary outcome was the Ocular Surface Disease Index (OSDI). Secondary outcomes included the Visual Analog Scale (VAS) for subjective symptoms, quality of life (QoL), the Schirmer I test (SIT), and general assessment. All outcomes were measured at baseline (Week 0), post-treatment (Week 4), and follow-up (Week 6).
Results
No statistically significant between-group differences were found in OSDI scores at Weeks 4 and 6 compared to baseline (p = 0.262, p = 0.105). Similarly, changes in VAS, QoL, and SIT scores showed no significant differences between groups (all p > 0.05). No serious adverse events occurred in either group.
Conclusion
Intradermal acupuncture showed comparable effectiveness to body acupuncture in relieving symptoms of moderate to severe DED, suggesting its potential as an alternative therapeutic option. While between-group differences were not definitive in this pilot study, the findings provide preliminary estimates to inform a future, properly powered non-inferiority trial aimed at determining whether IA can achieve clinically comparable outcomes with potential advantages in convenience and adherence.
Journal
Journal of Pharmacopuncture
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3831/KPI.2025.28.4.301
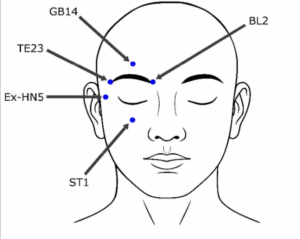
Verwendete Punkte:
- Blase 2
- Gallenblase 14
- Dreifach Erwärmer 23
- Magen 1
- Extrapunkt Kopf/Nacken 5 (EX-HN5)
QUELLE:
Park, S.-Y. (2025). Intradermal acupuncture for moderate to severe dry eye disease: a pilot randomized controlled trial. Journal of Pharmacopuncture, 28(4), 301–310. https://doi.org/10.3831/KPI.2025.28.4.301